F1.1 Identify various methods of payment that can be used to purchase goods and services.
Skill: Identifying Various Methods of Payment That Can Be Used to Purchase Goods and Services
Beginning in the Junior Division, students learn about the different methods of payment they can use to purchase various goods
and services. A method of payment is the means by which a payment is made.
Students can use the questions below to assess which methods of payment would be appropriate.
- What method of payment does the business accept?
- What method of payment is convenient?
- Which method of payment is safe (secure)?
- What method of payment is available to me?
|
Method of Payment |
Description and Requirements for Using this Method of Payment |
|
Cash  |
It is money in the form of bills or coins that is immediately available to buy goods or pay for services. |
|
Cheque 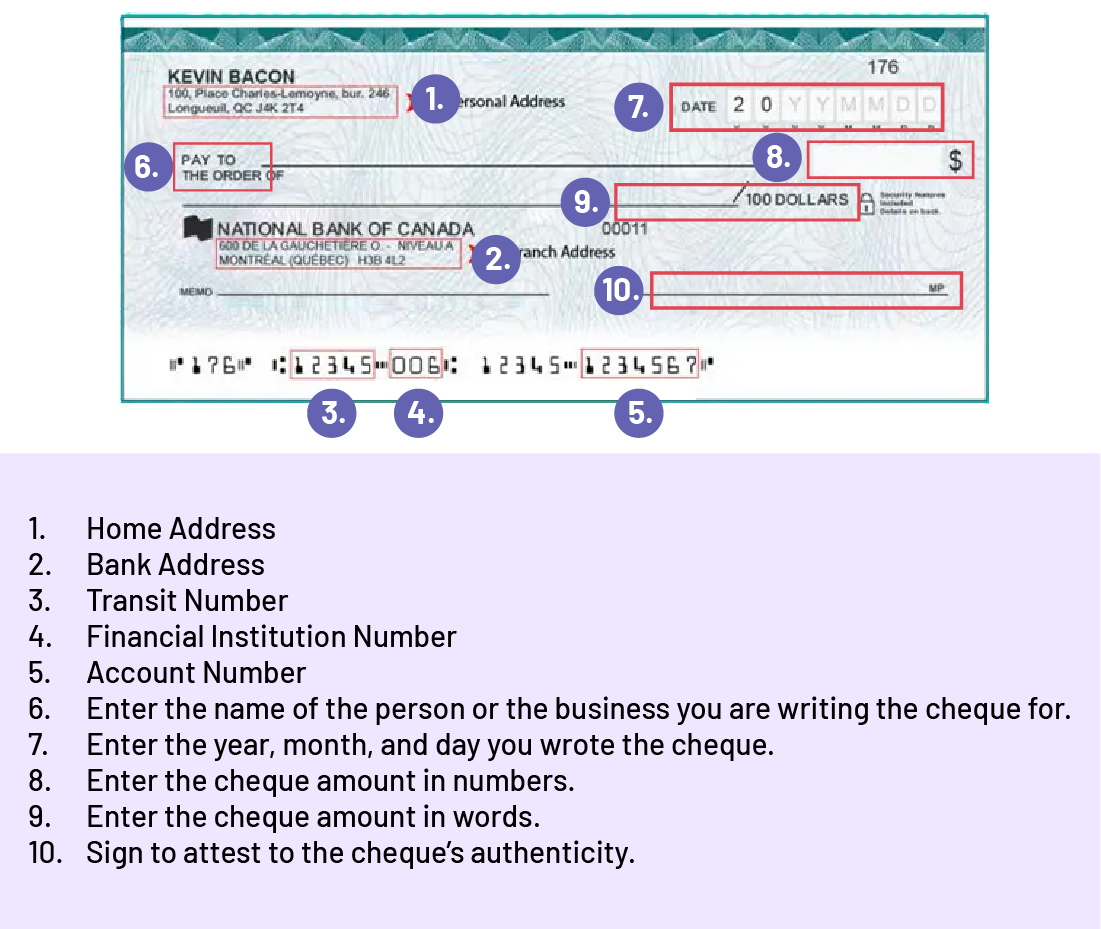
At the top left ‘the Home address Middle left: the address of the bank branch. At the bottom of the check: transit number, institution number and account number. Space to enter the name of the person or company to whom the check is issued. Top right: enter the date, month, and day the check is written. Under the date, enter the numerical amount of the check. In the middle of the check, the amount in words. Bottom right: enter your signature to certify the authenticity of the check. |
It is a paper document that instructs a financial institution to pay a certain amount of money from the person who holds the bank account to the person or institution named on the cheque (payee). The cheque is taken to the bank – or deposited electronically – for the transfer of cash to the payee for a purchased item. There may be a delay of a few days for the transaction to be finalized. In order to have and use personal cheques, you must have an account at a financial institution. Once you have a chequing account, you can order cheques. You will find the following information on most Canadian cheques:
When you write a cheque to another person or business, you need to make sure you have the money in your bank account. A cheque is considered cash that you already have. A person may use a cheque because they are paying a large amount of money and do not want to carry a large amount of cash. You make a cheque out to the payee by writing their name on the cheque. You must be careful because if you don't write anything down and the cheque is lost or stolen, someone can write their name on the cheque and deposit it into their own bank account. A cheque is also useful for paying others on a regular basis. For example, when paying rent every month. When you write a cheque, you must put the date on the cheque. You can write post-dated cheques, which means that the date you put on the cheque is the date from which it can be cashed. In Canada, a personal cheque is considered stale-dated 6 months after the date it was issued, and is not valid, unless it is a certified or When using cheques, you must pay special attention to how you account for them. This means you must make sure that the exact amount you want to transfer to the payee(s) is correct. You must also keep track of them so that you have a current bank balance. If your payee withdraws more money than you have in your bank account, you will have to pay additional fees. Source: Government of Canada. |
|
Barter/Trade  |
Barter is when two people exchange goods or services without using money. If you don't have the money to pay for a good or service, you can offer a trade for another good or service. For example, one person mows their lawn as well as their neighbour's in the summer, then the neighbour reciprocates by plowing both driveways in the winter. |
|
Debit Card  |
It is a payment card that withdraws money directly from the bank account to which it is linked. Most retail stores accept debit cards, which makes shopping easy and convenient. As with all methods of payment, you should carefully record your purchases and debit card use. Debit cards are safe to use, but there are instances where you may be vulnerable to theft. Protecting your Personal Identification Number (PIN) is especially important. Change it regularly and use discretion when using it in public. Source: Government of Canada. |
|
Credit Card  |
A credit card is a card issued by a financial institution that allows you to borrow money on a short-term basis to purchase goods and services. Institutions that issue credit cards charge interest if their customers do not pay the loan by the agreed-upon deadline. Some credit cards come with fees, such as an annual fee. Some credit card issuers offer rewards for purchases made with the card. All transactions are recorded and a single statement is sent on the same date each month showing the total amount to be repaid. Students need to understand that credit does not give them more money to spend. The money to pay off a credit card should be part of their budget. Note: Age Restrictions At the age of majority, which is 18 in Ontario, a person can have their own credit card without an adult co-signer. Source: Government of Canada. |
|
Gift Card  |
It is a magnetic or smart card issued by a business and holds a specific value or amount which can be used to purchase goods or services from that business. Gift cards are provided when payment is made before an actual item is selected or purchased. Businesses have immediate access to the money before releasing the inventory. |
|
Electronic Wallet  |
It is an electronic device (for example, smartphone or smartwatch) that can be attached to a bank account and allows payments to be made directly at the terminal. |
|
Electronic Transfer  |
It is a banking service that allows the transfer of funds between accounts affiliated with participating financial institutions via email or online banking. Note: There are sometimes fees associated with using electronic transfers. |
|
Cryptocurrency  |
It is virtual or digital money that is secured by cryptographic processes. |
Knowledge: Methods of Payment
A method of payment is a means, accepted by the seller, that a buyer uses to pay the seller for a good or service.
Depending on the student's situation and preferences, the idea of the best method of payment may differ. By learning about the different methods of payment people use to purchase goods and services, students will be able to develop consumer awareness and understand the factors that influence the choice of the method of payment.
It is critical to be aware of our own position as teachers. We need to regularly reflect on our preconceptions about the finances of those around us. We should reflect on our responses to questions such as, "Does the general population have access to all methods of payment?"
Not everyone has access to all methods of payment for many reasons. For example, some people may have credit restrictions or have values that payments must be made in cash. As teachers, we need to consider the complexity and diversity of student realities.
Knowledge: Goods and Services
A set of tangible and intangible products resulting from economic activity that are intended to satisfy needs. A distinction is made between goods, which are material and tangible, and services, which are intangible and must be consumed immediately.
