F1.1 Describe some advantages and disadvantages of various methods of payment that can be used when dealing with multiple currencies and exchange rates.
Skill: Describing Some of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Methods of Payment for Dealing With Multiple Currencies and Exchange Rates
Students, having the knowledge of various methods of payment, multiple currencies, and exchange rates, think critically to describe the advantages and disadvantages of each, as they consider different situations.
Methods of payment should be considered before making purchases involving currency conversion. Understanding how to make payments in another country's currency increases knowledge of money concepts.
Students use the mathematical processes of reasoning and proving, reflecting, representing, and selecting of tools and strategies to work on their understanding of the most appropriate method of payment for the multiple currency situation.
As students deepen their understanding of how to use different methods of payment to their advantage when purchasing in different currencies, offer the questions below as guidelines:
- Which method of payment allows me to benefit from the lowest exchange rates?
- What costs are associated with using different methods of payment?
- What is the safest way to pay in foreign currency?
- Depending on the purchase I am making, what do I need to consider when choosing the different methods of payment?
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Methods of Payment for Foreign Currency Purchases
| Method of Payment | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Cash  |
|
|
|
Debit Card  |
Note: It is important to contact your bank and determine if your debit card charges foreign transaction fees. |
|
|
Credit Card  |
|
|
|
Electronic Transfer  |
|
|
|
Cryptocurrency  |
|
|
|
Gift Card  |
|
|
It is important that students have the opportunity to work through different scenarios of foreign currency purchases, and to consider the advantages and disadvantages of different methods of payment.
Let's look at two scenarios that students may encounter involving a foreign currency purchase.
Scenario 1
Students and their families may need to purchase currency to send to their families abroad.
Students should consider the following questions:
- What is the best method of payment to use when sending money abroad?
- Which method of payment will be the most economical?
- What method of payment will ensure that the money reaches the recipient safely?
- What do I need to know about the recipient's ability to receive the money?
Considering all possible methods of payment, electronic transfer is the safest and easiest way to ensure that the family member receives the money.
Students should research the fees and exchange rates of two banks, taking into account the amount of money the family member needs.
Scenario 2
Students are planning a trip to Luxembourg and need to determine the best methods of payment to budget for the trip.
They will need to think about purchasing euros to cover the cost of the trip such as: meals, excursions, hotel, insurance and any other potential purchases.
In this scenario, students may decide to use multiple methods of payment to cover all expenses during the trip.
For example, they may plan to cover some of their costs, such as insurance, by using a credit card, co-signed by their parents or legal guardians. Often, credit cards offer travel insurance with the annual fee. The students may find that the cost of the credit card will cover the cost of the travel insurance.
Students may also have a co-signed credit card with parents or legal guardians to cover emergency expenses and ensure that the credit card balance is sufficient.
Students can contact their local bank and inquire about the cost of using their debit card to access euros while traveling. If the cost of converting funds is optimal, with no additional fees, and knowing that ATMs will readily accept their debit card, students may choose this method of payment so they do not have to carry large amounts of cash.
Students may decide to purchase a small amount of euros to travel with, so that if cash is lost or stolen, it will be a small amount.
Please note that the minimum age to obtain your own credit card in Ontario is 18, but guardians or parents can be co-signers to obtain one. The co-signer agrees to be responsible for any outstanding balance, and any late payments made by the teen will appear on the co-signer's credit history.
Relevant and realistic learning contexts help to build financial and mathematical understanding and skills.
Knowledge: Method of Payment
A means that a buyer uses to pay the seller for a good or service that is also acceptable to the seller. Typical methods of payment may include cash, cheques, credit, or debit cards (note that there are age restrictions and conditions that must be met), electronic transfers, gift cards, and online payment services. Other examples of methods of payment include bartering, swapping (for example, trading cards), e-wallet (for example, passing one's smartphone or watch linked to a bank account to a terminal), and cryptocurrency.
There are different ways to pay in foreign currencies and each method has its advantages and disadvantages.
Before making a purchase that involves currency conversion, consider the methods of payment available in different currencies and the exchange rates.
Understanding the ways in which payments can be made in the currencies of other countries builds on previous knowledge of monetary concepts.
Knowledge: Currencies
A system of money used in a country typically includes coins and bills.
Note: The currencies of other countries are not equal in value to the Canadian dollar.
For the sake of simplicity and to establish an international standard where all currencies can be talked about anywhere in the world without language barriers, each currency has a three-letter acronym. Usually, but not as a general rule, the first two letters refer to the country and the third to the name of the currency.
For example, here are the abbreviations for the currencies of Canada, the United States, China and Peru:
- Canada: Canadian dollar, CAD
- United States: US dollar, USD
- China: Yuan (¥), CNY
- Peru: Sol, PEN
Knowledge: Currency Converters
Students can use the Bank of Canada's currency converter to convert currencies from other countries to Canadian dollars and vice versa by entering an amount of money in one country's currency to obtain the corresponding amount in another country's currency.
image Bank of Canada currency converter web page. Currency converter. The Bank of Canada website allows you to search for historical data for various currencies and the conversion rate in relation to the Canadian dollar. In a box: The Attention Panel. Bank of Canada exchange rates are only indicative rates based on the aggregated results of average exchange rate estimates from financial institutions. For more information, see the Terms of Use and Disclaimer. Conversions are based on Bank of Canada exchange rates, which are published each business day by 4:30 p.m. Eastern time. Amount and Currency: Amount: One. Starting Currency. Canadian dollar, U.S. dollar round trip arrow. Dates. Select the date range One week Convert.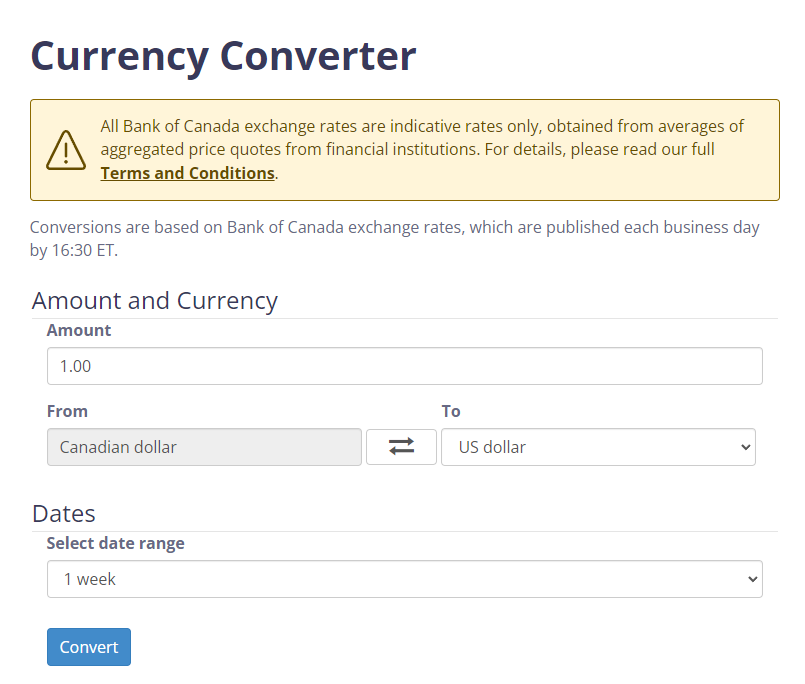
Source: Currency converter – Bank of Canada
Knowledge: Exchange Rates
An exchange rate shows how much it costs to buy units of one currency using another, and shows the relationship between the value of one country's currency to another.
