B1.5 Describe what makes an number even or odd.
Activity 1: The Characteristics of Even and Odd Numbers
Group students into teams of two. Give each team a collection of 6 to 40 objects (for example, blocks).
Ask the members of each team to divide the objects equally.
Ask the following questions:
- Is it still possible to share the objects equally?
- Why?
Write, on the interactive whiteboard or a large sheet of paper, the numbers that students were able to divide equally and the numbers that they were unable to divide equally.
Example
| Number that can be equally divided by two (without remainder) | Number that cannot be equally divided by two (with remainder) |
|---|---|
| 28 | 17 |
| 22 | 33 |
| 16 | 29 |
| 34 | 15 |
| 10 | 31 |
Ask students questions such as:
- If we compare the numbers in the two columns of the table, what do we notice? What can we conclude?
- What are the even numbers? What are the odd numbers? How do you know?
Support students to notice the following regularity: numbers ending in 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9 are odd numbers and numbers ending in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8 are even numbers.
Invite students to place the numbers below in the correct column according to whether they are even or odd.
| 37 | 30 | 32 | 14 | 19 | 18 | 11 | 7 |
Activity 2: Equal Numbers or Not?
Show pictures of objects grouped in two rows or columns to students, such as:
Examples
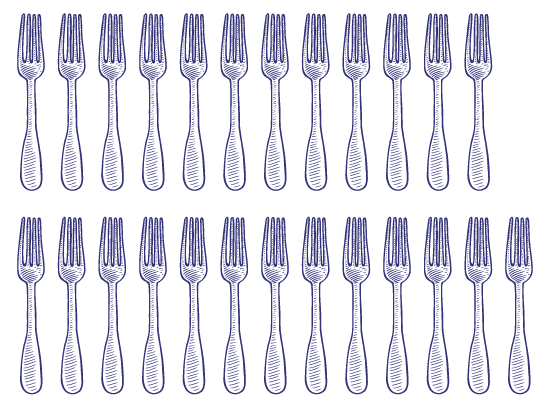



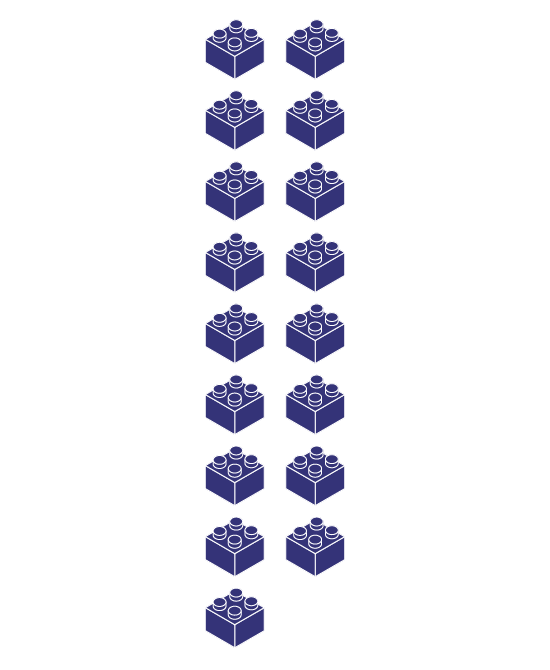
Ask students whether the pictures show equal or unequal groups.
Ask students questions such as:
- Do these pictures show equal groups? How do you know?
- What common characteristics do you notice across all of the pictures? How do the pictures differ?
- When comparing the two columns or rows of objects, what do you notice?
Explain to students that equal groups (without remainder) represent even numbers and that groups that are not equal (with remainder) represent odd numbers.
Group students into teams of two. Give each team a number between 11 and 60. Ask students to determine whether their number is even or odd by explaining their reasoning using materials or drawings and words.
