B2.5 Add and subtract fractions, including by creating equivalent fractions, in various contexts.
Activity 1: The Decisive Fraction (Addition and Subtraction of Equivalent Fractions)
Prepare a series of scenarios involving the addition and subtraction of fractions. Divide students into teams of four. Distribute one scenario at a time. Each team must propose two ways to solve the problem. Ask them to compare their strategies and decide which one they think is the most effective. Students must justify their choice. Give feedback to the class so that the students can verbalize their analysis and observations.
Example Scenarios
Example 1
During a race, at \(\frac{1}{4}\) of the course, the runner takes an energy drink. The other refreshment point is \(\frac{2}{8}\) further down the course. What fraction of the race does he have left to run after the second refreshment point?
Example 2
Grade 7 students propose a plan for the schoolyard to the school principal. They divide the playground into different areas.
- Garden: \(\frac{1}{{10}}\) of the yard area
- Soccer field: \(\frac{6}{{15}}\) of the yard area
- Playground: \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the yard area
What fraction of the yard area is included in the student development plan?
Example 3
On a typical day in the school calendar, Olivia sleeps \(\frac{3}{8}\) of her day and spends \(\frac{1}{3}\) of her day at school. Also, she dances during \(\frac{1}{{12}}\) of it. What fraction of the day does she have left to do something else?
Example 4
The carpenter needs to cut three boards to make a border for a garden that is behind a shed. Two of the boards are \(5\frac{3}{4}\) dm each and the other is \(7\frac{2}{{16}}\) dm. What is the total length of the three boards?
Activity 2: Which One Doesn't Belong? (Addition and Subtraction of Equivalent Fractions)
Prepare a PowerPoint with examples that includes four images representing addition and subtraction situations involving fractions. The students must decide which image they think doesn't belong, take a stand, and justify their reasoning. Students should share in small groups or as a class. It's important to listen to students' comments to check their understanding.
Note: There are several possibilities.
Example 1
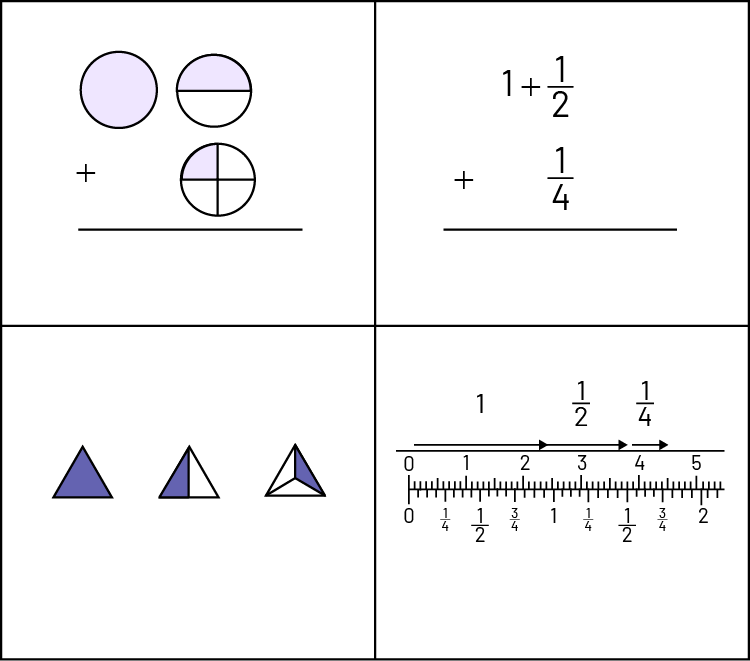
Possible student rationales:
- The image on the bottom left does not belong, because it is not equivalent to the other 3.
- The content in the top right box does not belong, as the representation is only symbolic.
- Other possibilities.
Example 2

Possible student rationale:
- The top right image does not belong, because for each of the other images, if we add the fractional parts together we get a whole equal to 1, but not that one.
Source: Inspired by the site https://wodb.ca
