E1.4 Give and follow multistep instructions involving movement from one location to another, including distances and half- and quarter-turns.
Activity 1: Slide, Slide (Giving and Following Directions)
Instructions
Present a grid on a whiteboard.
Place a triangle on a starting square and draw its outline in blue.
Ask a student to place a small red octagon on another square to indicate the finish square.
Ask them to give directions to another student to move the triangle to the finish square.
Draw the outline of the triangle in red in the finish square.
Point out that the triangle has slid to the finish square.
Explain that the triangle drawn in blue is the initial shape and the triangle drawn in red is the image.
Perform the same type of movement with other teams of two students.
Teacher Moves
Ensure that the student describes the movement, namely, getting from the starting square to the ending square by giving the direction and distance.
Point out the shortest paths and the paths that have movements in all four directions.
Point out that the initial shape is always congruent with its image.
Note: Different strategies can be used to test understanding of the concept of translation.
For example:
- Draw the initial shape and give the movement. Ask to find the image.
- Draw the image and give the movement. Ask to find the initial shape.
- Draw the initial shape and the image. Ask them to find and describe the movement.
Source: translated from Guide d’enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 1re à la 3e année, Géométrie et sens de l'espace, p. 68-69.
Activity 2: Mystery Number
Give each pair a hundred chart and a token.
A student places the token on a number.
The other student shows them a sequence of arrows:
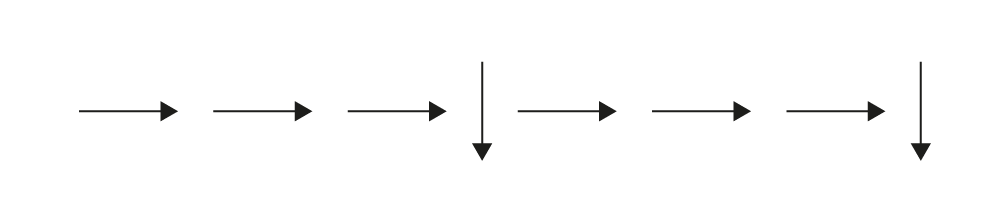 Image Eight arrows in a row. The first three arrows point to the right, one arrow points down, three arrows point to the right, the last arrow points down.
Image Eight arrows in a row. The first three arrows point to the right, one arrow points down, three arrows point to the right, the last arrow points down.
The student who placed the token makes the moves and finds the mystery number. Ask students to take turns inventing other sequences of arrows.
This activity can integrate content from the Algebra strand as the student creates non-numerical sequences.
Source: translated from Guide d’enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 1re à la 3e année, Géométrie et sens de l'espace, p. 133.
Activity 3: Give and Follow Directions to Make a Trip
At school, there is a Bike Rodeo activity in the main yard to teach students to look both ways before crossing the street when riding their bikes in their neighbourhood.
Using the map below, mark a route that includes a starting point, stop signs at all street corners and finishing at the starting point. At each stop, give the necessary instructions to continue the route.
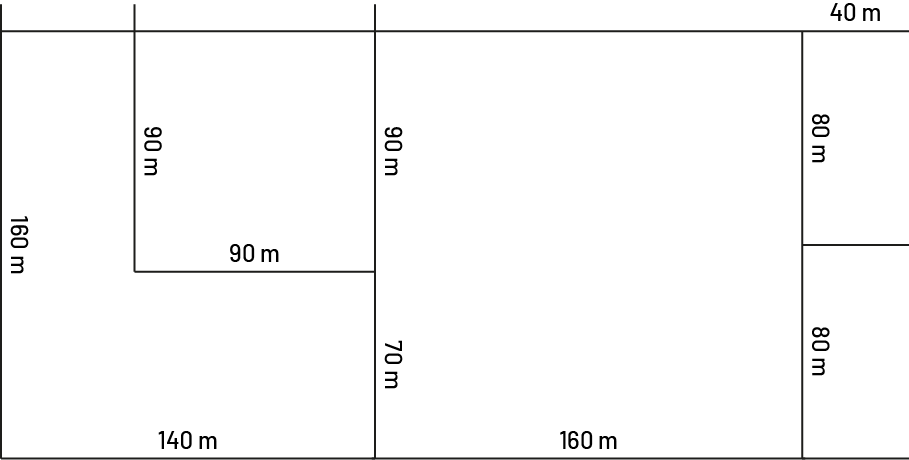

Source: translated from En avant, les maths!, 3e année, CM, Sens de l’espace, p. 18.
Activity 4: Movements and Sum
Little Fish is swimming around the lake, and there are numbers on the lake bed. Write the movements Little Fish must make to lay her eggs on two numbers whose sum will be 550.
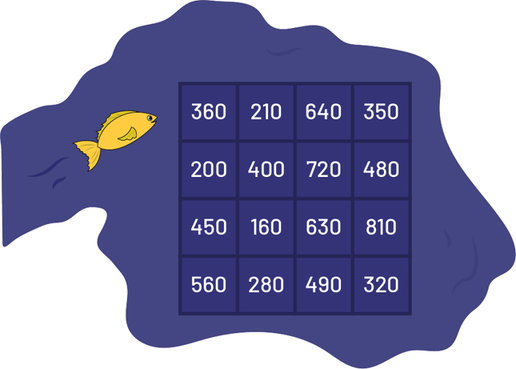 Image A fish enters a lake. It's heading towards a grid made up of 4 columns and 4 rows. The numbers in the boxes are as follows: 360, 210, 640, 350, 200, 400, 720, 480, 450, 160, 630, 810, 560, 280, 490, 320.
Image A fish enters a lake. It's heading towards a grid made up of 4 columns and 4 rows. The numbers in the boxes are as follows: 360, 210, 640, 350, 200, 400, 720, 480, 450, 160, 630, 810, 560, 280, 490, 320.
Source: translated from En avant, les maths!, 3e année, CM, Sens de l’espace, p. 22.
