E1.1 Identify geometric properties of triangles, and construct different types of triangles when given side or angle measurements.
Activity 1: Can We Create a Triangle?
Place straws of various lengths in an opaque bag. Place straws of the same length in the same bag. Have students take turns drawing three straws from the bag. Ask them to explain how they can use the lengths of the straws to determine if it is possible to construct a triangle using the three straws. If a triangle can be constructed, ask them to identify the type of triangle.
Source: translated from Guide d'enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 4e à la 6e année, Géométrie et sens de l'espace, Fascicule 1, p. 64.
Activity 2: Hidden Triangles
In the shape below, how many of each of the following types of triangles are there?
- equilateral triangles
- isosceles triangles
- scalene triangles
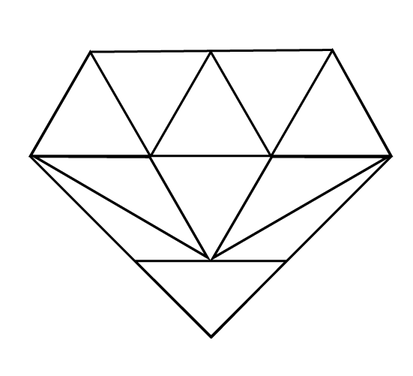
Note: There are 7 equilateral triangles, 12 isosceles triangles (5 with two congruent sides and 7 with three congruent sides) and 6 scalene triangles.
Source: translated from Guide d'enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 4e à la 6e année, Géométrie et sens de l'espace, Fascicule 1, p. 65.
Activity 3: An Arrangement of Triangles
Have students create an arrangement of triangles and label the types of triangles used. Point out that they can use a variety of materials and means to make their creation (for example, straws, coffee stir sticks, paper or cardboard strips, drawing, dynamic geometry applications). The final product may be, for example, a mobile, a poster, a drawing, a puzzle, a collage, etcetera.
Source: translated from Guide d'enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 4e à la 6e année, Géométrie et sens de l'espace, Fascicule 1, p. 64.
