B1.7 Read, represent, compare, and order decimal tenths, in various contexts.
Activity 1: If...
Place pieces of the base ten material in a bag. Remove one or more pieces and ask questions based on the pieces removed.
Example of a piece removed from the bag
A rod

Sample question
- If this rod is the whole, how do you represent a tenth? (The small cube represents a tenth of a rod)
Example of a piece removed from the bag
A large cube
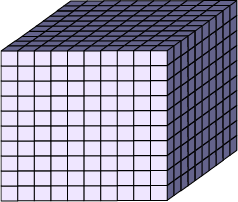
Sample question
- If this large cube is the whole, how do you represent a tenth? (The flat represents a tenth of the large cube)
Example of a piece removed from the bag
A flat

Sample question
- If this flat represents one ten, how do you represent four tenths? (Since the flat represents one ten, a rod is one whole. So four small cubes represent four tenths of a rod)
Example of pieces removed from the bag
Twelve rods

Sample question
- If a rod represents one tenth of a whole, what do these 12 rods represent? (Since one rod represents one tenth of a whole, a flat is one whole. So the 12 rods represent 1 flat and 2 tenths of a flat)
Source: translated from Guide d'enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 4e à la 6e année, Numération et sens du nombre, Fascicule 3, Nombres décimaux et pourcentages, p. 145.
Ask students to represent the answers using symbols, pictures, base ten material or words.
Activity 2: Which Number is Closest to the Target?
This activity is done in pairs using two dice. One student determines the target by rolling the first die and then the second die. The number on the first die represents the number of wholes and the number on the second die represents the number of tenths (for example, a 4 followed by a 6 would be 4.6). Next, each student rolls the two dice and must use the numbers on the dice to create their number (for example, getting 6 and 3 with the dice, the student could create 6.3 or 3.6). Each student names their number using the appropriate terminology (for example, 3 and 6 tenths) and then together they determine which of the two numbers is closer to the target. Students can use a variety of number representations (for example, concrete materials, number line) or a calculator to do this. The student whose number is closest to the target gets a point. Students repeat the process nine more times, and the student with the most points wins the game.
Source: translated from Guide d'enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 4e à la 6e année, Numération et sens du nombre, Fascicule 3, Nombres décimaux et pourcentages, p. 146.
