B2.2 Recall and demonstrate multiplication facts for 1 × 1 to 10 × 10 and related division facts.
Activity 1: Sometimes Upside Down?
Directions
Ask students to represent \(5\; \times \;8\) and \(8\; \times \;5\) using arrays.
Here are some examples of possible representations:

Proceed in the same way with various multiplications of two numbers.
Teacher Moves
Ask questions to help understand the commutative property of multiplication, such as:
- What do you see?
- How many counters are there? rows? columns?
- I rotate the array 90° (as if it falls over). How many are there now?
- What is the product of 5 and 8? What other multiplication fact resembles this?
- By rotating the arrays, what other pairs of numbers give the same product?
Source: translated from Guide d'enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 1re à la 3e année, Numération et sens du nombre, p. 41-42.
Activity 2: The Big Race
Targeted Strategies: + 1, + 2, + 0, - 0, doubles, numbers close to doubles, grouping by tens
Material
- Appendix FR22 (The Big Race game sheet) (one per student)
- pencils
- counters
The big race can be used to familiarize students with all the strategies related to multiplication in a paper-and-pencil exercise. Each student needs a copy of the game sheet. Students write the strategy to be used to complete the game sheet in the centre box, then move around the track applying this strategy to each of the numbers around the track, writing their answer in the outer box of the game sheet. (Counters should be made available for students to use)
This game is ideal for practising strategies as they are being taught as well as reviewing previously learned strategies.
Source: translated from Guide d'enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la maternelle à la 6e année, Fascicule 5, p. 80.
Activity 3: Array (Multiplication Facts)
Represent, with students, the basic number facts being studied using arrays.
Collectively create a large poster that illustrates basic number facts.
The poster can be created with different colours.
Ask students to identify patterns and connections between products.
Be sure to have a standard multiplication table as well that students can reference, as shown below.
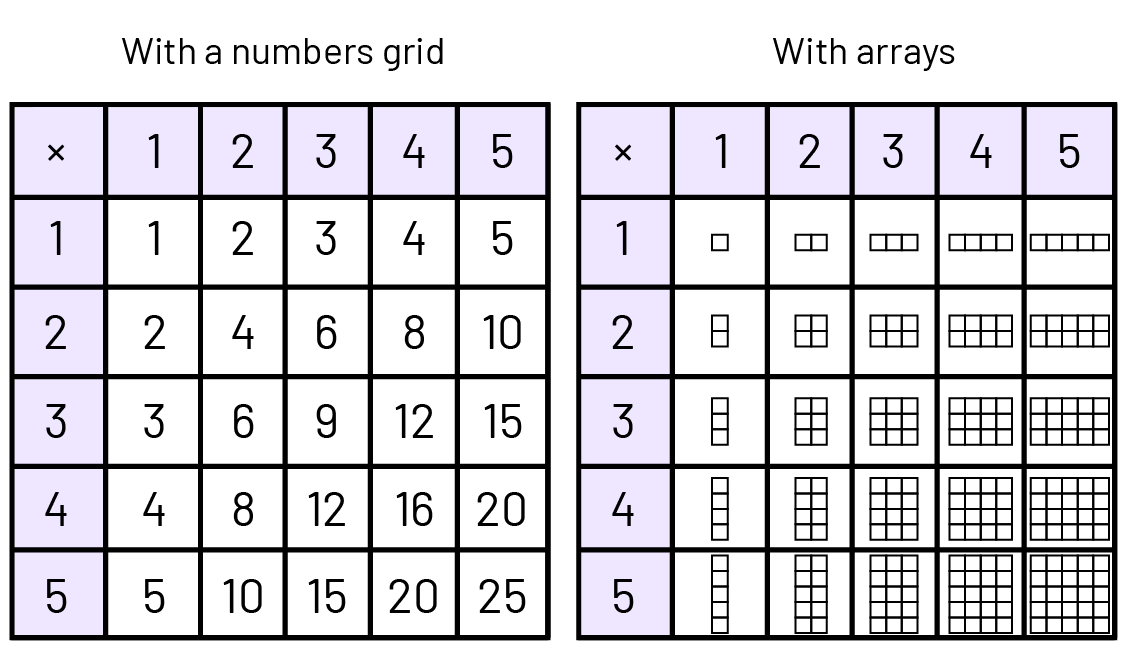
Activity 4: Multiply or Add Game
Number of players: 2
Material 2 dice
Explain the following scenario to the students:
Roll the 2 dice, then add or multiply the 2 numbers. If you choose, for example, to add, you must always add and your partner must always multiply. If you choose to multiply, your partner will add. The winner is the one who reaches 12.
Ask, "If you start first, which operation will you choose and why?
Source: translated from L'@telier - Ressources pédagogiques en ligne (atelier.on.ca).
