B1.2 Read and represent integers, using a variety of tools and strategies, including horizontal and vertical number lines.
Skill: Reading Whole Numbers
Each integer has an opposite, located an equal distance on the opposite side of zero on the number line. For example, - 1 and 1 are opposite integers and are at the same distance from zero.
When combined, pairs of opposite integers equal zero. For example, integer pairs like \({(+ 3)}\;{\rm{and}}\;{(- 3)}\; = \;0\).
The zero is defined as being neutral, and therefore neither is positive nor negative.
Negative integers are "less than zero". Zero is exactly in the centre of the number line of integers; the line is symmetrical about zero.
On a horizontal number line, positive integers are displayed to the right of zero and negative integers are displayed to the left of zero.
On a vertical number line, positive integers are displayed above zero and negative integers are displayed below zero.
Source: The Ontario Curriculum, Mathematics, Grades 1-8, Ontario Ministry of Education, 2020..
The most common use of negative integers is for temperature. For example, - 3ºmeans 3º below 0 degrees. Sometimes negative integers are used to describe debts. For example, if one owes $5, one can think of it as having - $5. Negative numbers are also sometimes used in field hockey statistics and golf scoring.
Source: translated from Réduction des écarts de rendement, 9e année, p. 11.
Skill: Representing Whole Numbers
Negative integers are located to the left of 0 on the number line. They are the opposites of the positive integers, which means that they are located as far to the left of 0 as the positive integers are to the right of 0. Thus, -5 is exactly the same distance to the left of 0 as 5 is to its right. Since the numbers are placed in ascending order from left to right on the number line, a negative integer is therefore necessarily smaller than a positive integer.

It is possible to represent the integers on a vertical number line that is similar to a thermometer rather than on a horizontal number line. In this case, the positive integers are above the negative integers.
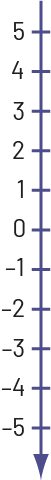
It is also possible to use two-coloured counters to represent whole numbers, one color to represent positive whole numbers and another to represent negative whole numbers. For example, 5 can be represented by 5 white counters and -5 by 5 red counters.

Source: translated from Réduction des écarts de rendement, 9e année, p. 10-11.
Integers can be represented as points on a number line, or as vectors that shows magnitude and direction. The integer −5 can be shown as a point positioned 5 units to the left of zero or 5 units below zero. The integer − 5 can also be shown as a vector with its tail positioned at zero and its head at −5 on the number line, to show that it has a length of 5 units and is moving in the negative direction.
Source: Ontario Curriculum, Mathematics Curriculum, Grades 1-8, 2020, Ontario Ministry of Education.
Knowledge: Integers
Set of integers (\(\mathbb{Z}\))
The set of integers is made up of whole numbers (0, 1, 2, 3…) and negative integers (- 1, - 2, - 3…). We can therefore say that all whole numbers are integers, but not all integers are whole numbers. The relationship between whole numbers and integers can be represented by the Venn diagram shown below.

Source: translated from Guide d’enseignement efficace des mathématiques de la 4e à la 6e année, Numération et sens du nombre, Fascicule 2, Fractions, p. 41.
